Hydrogen acetate (hydrogen acetate formula)
Hydrogen acetate, also known as acetic acid or ethanoic acid, is an organic carboxylic acid mainly known for being the main component of vinegar.
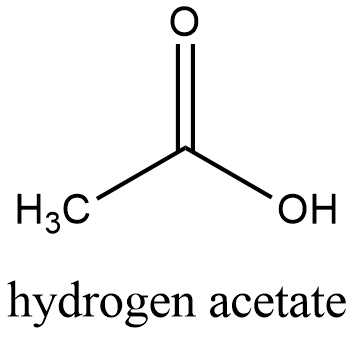
Formula and structure: The chemical structure of the hydrogen acetate is CH3COOH and its molecular weight is 60.05 g/mol. It is the second most simple carboxylic acid with only two carbon atoms in its skeleton. It is formed by one methyl group (-CH3) that has the a sp3 or tetrahedral conformation and one carboxylic carbon (-C=O) with has a conformation sp2 or planar. To the carboxylic carbon, a second oxygen is bond but with a simple bond (-C-O). Its chemical structure can be written as below, in the common representations used for organic molecules.
Occurrence: Hydrogen acetate is produced by bacteria and yeast during the fermentation of sugars, particularly, the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is highly used for preparing these fermentations.
Preparation: Hydrogen acetate is prepared from methanol carboxylation, in a reaction in a reaction between the methanol and carbon monoxide.
One part of the world production of hydrogen acetate comes from bacterial fermentation, specially for preparing vinegar, it is used the hydrogen acetate produced by microbes in order to get a higher purity for human consume.
Physical properties: Hydrogen acetate is a colorless liquid with corrosive pungent vinegar-like odor with a sour taste. Its density is 1.05 g/mL, and its melting and boiling point are 16 ºC and 118 °C, respectively. It is highly miscible in water, methanol and ethanol. Vinegar is prepared as a solution of 5% of hydrogen acetate in water.
Chemical properties: Hydrogen acetate is a weak organic acid, which means that it is not completely dissociated in water when a solution of this compound is prepared and its reaction should be represented as a reversible reaction:
CH3CO2H → CH3CO2− + H+
The pH of solution of hydrogen acetate is not too low and it oscillated between 3-5.
Its highly miscibility in water is due to the formation of hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atoms and the hydrogen atoms of the water.
Uses: Hydrogen acetate is largely used in the food industry, where a solution of 5% is used as vinegar. It is also very used to prepare buffer solutions along with sodium acetate for regulating the pH of solutions. Moreover, it is also used in synthesis for producing thousands of valuable compounds as vinyl acetate monomers. Hydrogen acetate is also used as a solvent.
Health effects/safety hazards: when concentrate, hydrogen acetate is very corrosive to eyes, skin and mucous membranes upon inhalation or contact. It can cause severe damage on the eyes and it is flammable over temperatures of 40 ºC.
|
Related Links: |
