The First Derivative Rule
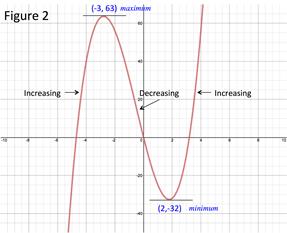
Figure 1 is the graph of the polynomial function 2x3 + 3x2 - 30x.
The first derivative of a point is the slope of the tangent line at that point. When the slope of the tangent line is 0, the point is either a local minimum or a local maximum. Thus when the first derivative of a point is 0, the point is the location of a local minimum or maximum.
FIRST DERIVATIVE TEST:
Suppose that c is a point such that the first derivative is 0, f '(c) = 0
- If f 'changes from positive to negative at c, then c is a local maximum.
- If f 'changes from negative to positive at c, then c is a local minimum.
- If f ' does not change at c, no minimum/maximum exists at c.
Because the derivative is the slope of the tangent line, if the derivative is positive that means the slope is positive and the function is increasing. Likewise if the derivative is negative the slope is negative and the function is decreasing. Therefore we have a test to determine if an interval is increasing or decreasing.
If the first derivative is positive on an interval, the function is increasing on this interval. If the first derivative is negative on an interval, the function is decreasing on this interval.
INCREASING/DECREASING TEST:
- If f ' > 0 on an interval, the function is increasing on that interval.
- If f ' < 0 on an interval, the function is decreasing on that interval.
Let's look at some examples.
|
Step 1: Find the values of x when the first derivative is 0, . |
Find the first derivative: f(x) = 2x3 + 3x2 - 36x
Set the derivative equal to zero: 0 = 6x2 + 6x - 36 Factor: 0 = 6(x2 + x - 6) 0 = 6(x + 3)(x - 2)
Set each factor to zero and solve: 6 ≠ 0 x + 3 = 0; x = -3 x - 2 = 0; x = 2 |
||||||||||||||||
|
Step 2: Create a table of intervals that end/begin with x-values such that Take the x-values found in Step 1 and create an interval table. To determine the sign of the first derivative select a number in the interval and solve. If the first derivative on an interval is positive, the function is increasing. If the first derivative on an interval is negative, the function is decreasing. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Step 3: Apply the first derivative test to determine the minimum/maximum points. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
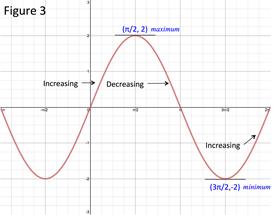
Because the first derivative changes from positive to negative at -3, there is a local maximum at -3. The maximum value at that point is: Local maximum: (-3, 63) Because the first derivative changes from negative to positive at 2, there is a local minimum at 2. The maximum value at that point is: Local minimum: (2, -32)
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Step 1: Find the values of x when the first derivative is 0, . |
Find the first derivative:
Set the derivative equal to zero: 0 = 2 cos x Solve for x: 0 = cos x
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Step 2: Create a table of intervals that end/begin with x-values such that . Take the x-values found in Step 1 and create an interval table. To determine the sign of the first derivative select a number in the interval and solve. If the first derivative on an interval is positive, the function is increasing. If the first derivative on an interval is negative, the function is decreasing. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Step 3: Apply the first derivative test to determine the minimum/maximum points. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
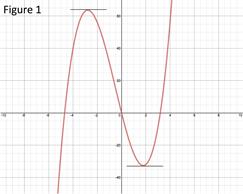
Because the first derivative changes from positive to negative at , there is a local maximum at . The maximum value at that point is: Local maximum: Because the first derivative changes from negative to positive at , there is a local minimum at . The maximum value at that point is: Local minimum:
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Related Links: Math algebra The Second Derivative Rule L'Hospital's Rule Pre Calculus |
To link to this The First Derivative Rule page, copy the following code to your site: