Finding Intercepts of Rational Fractions
To find the y-intercept(s) (the point where the graph crosses the y-axis), substitute in 0 for x and solve for y or f(x).
To find the x-intercept(s) (the point where the graph crosses the x-axis â also known as zeros), substitute in 0 for y and solve for x.
Examples: Find the intercepts of the function given.
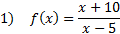
To find the y-intercept, we must substitute in 0 for each x:
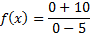
And then simplify:
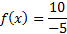
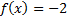
There is a y-intercept at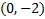 . (Notice that 0 is the x coordinate because on the y-axis, x = 0.)
. (Notice that 0 is the x coordinate because on the y-axis, x = 0.)
To find the x-intercept, we must substitute in 0 for y or f(x):
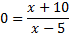
And then solve by cross-multiplying:
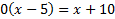
0 = x + 10
x = -10
There is a y-intercept at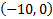 . (Notice that 0 is the y coordinate because on the x-axis, y = 0.)
. (Notice that 0 is the y coordinate because on the x-axis, y = 0.)
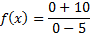
And then simplify:
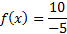
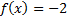
There is a y-intercept at
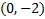 . (Notice that 0 is the x coordinate because on the y-axis, x = 0.)
. (Notice that 0 is the x coordinate because on the y-axis, x = 0.)To find the x-intercept, we must substitute in 0 for y or f(x):
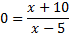
And then solve by cross-multiplying:
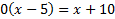
0 = x + 10
x = -10
There is a y-intercept at
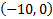 . (Notice that 0 is the y coordinate because on the x-axis, y = 0.)
. (Notice that 0 is the y coordinate because on the x-axis, y = 0.)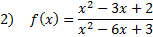
To find the y-intercept, we must substitute in 0 for each x:
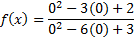
And then simplify:
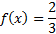
There is a y-intercept at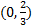 .
.
To find the x-intercept, we must substitute in 0 for y or f(x):
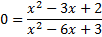
And then solve by cross-multiplying:
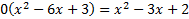
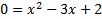
We must now solve the quadratic either by factoring or by using the quadratic formula.
We can factor this trinomial, so we'll use that method:
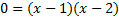


There are y-intercepts at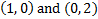 .
.
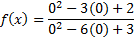
And then simplify:
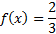
There is a y-intercept at
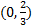 .
. To find the x-intercept, we must substitute in 0 for y or f(x):
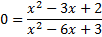
And then solve by cross-multiplying:
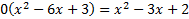
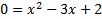
We must now solve the quadratic either by factoring or by using the quadratic formula.
We can factor this trinomial, so we'll use that method:
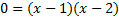


There are y-intercepts at
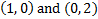 .
. Note: Not all rational functions have both an x or y intercept. If you cannot find a real solution, then it does not have that intercept.
Practice: Find the x and y intercepts of each rational function:
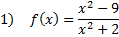
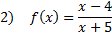
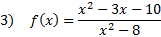
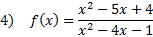
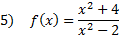
Answers: 1)x-int.
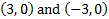 y-int.
y-int. 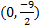 2) x-int. (4, 0) y-int.
2) x-int. (4, 0) y-int. 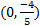 3) x-int. (-2, 0) and (5, 0) y-int
3) x-int. (-2, 0) and (5, 0) y-int 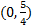 4) x-int. (1, 0) and (4, 0) y-int (0, -4) 5) x-int: none y-int: (0, -2)
4) x-int. (1, 0) and (4, 0) y-int (0, -4) 5) x-int: none y-int: (0, -2)
|
Related Links: Math Fractions Factors |
