Charles' Law Formula
Charles' Law shows the relationship between the Temperature and Volume of a gas. Temperature and volume have a direct relationship, so if the volume goes up then the temperature goes up and if the temperature goes down then the volume goes down (and vice versa)
The equation for Charles' is:
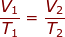
T1 = Initial Temperature (Kelvin - K)
V1 = Initial Volume (L or mL)
T2 = Final Temperature (Kelvin - K)
V2 = Final Volume (L or mL)
Note: Temperature must be in Kelvin for the equation to work. You calculate Kelvin temperature by adding 273 to the Celsius temperature.
Charles' Law Formula Questions:
1.) Calculate the decrease in temperature when 2.00 L at 20.0 °C is compressed to 1.00 L.
Answer: For this problem the Initial Volume is V1 = 2.00 L. The Initial Temperature is T1 = 20.0 + 273 = 293K. The Final Volume is V2 = 1.00 L and the Final Temperature (T2 ) is what you are asked to solve for.
Plug into the Charles' Law Equation
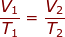
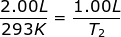
T2 = 146.5 K
The temperature decreased to 146.5 K.
2.) At 27.00 °C a gas has a volume of 6.00 L. What will the volume be at 150.0 °C
Answer: The Initial Volume is V1 = 6.00 L. The Initial Temperature is T1 = 27.00 + 273 = 300 K. The Final Temperature is T2 = 150.0 + 273 = 423 K. The Final Volume (V2) is what we are trying to find in the problem.
Plug into the Charles' Law Equation
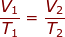
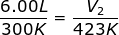
V2 = 8.46 L
The volume of the container would be 8.46 L.
