Copper (II) Nitrate Formula
Copper (II) nitrate, also known as cupric nitrate, is an inorganic salt known for its very brilliant blue color that is used as catalyst in several reactions.
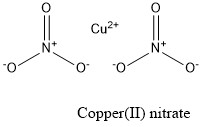
Formula and structure: Copper (II) nitrate chemical formula is Cu(NO3)2. The structure of the anhydrous salt is formed by one cation Cu2+ and two anions NO3-. The compound shows up to 5 different hydrate forms, being the trihydrated Cu(NO3)2.3H2O and the pentahydrated Cu(NO 3)2.5H2O salts the most common. The molar mass of the anhydrous form is 187.55 g mol-1 while the trihydrate form is 241.60 g mol-1. Its chemical structure can be written as below, in the common representations used for organic molecules.
Occurrence: Copper (II) nitrate and other copper nitrates are found in natural as part of some minerals as gerhardtite and rouaite.
Preparation: Copper (II) nitrate is prepared from metallic cupper treated with nitric acid. It can also be produced by treating metallic copper with dinitrogen tetroxide:
Cu + 4 HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2 H2O + 2 NO2
Cu + 2 N2O4 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2 NO
Physical properties: Copper (II) nitrate in all the hydrated forms is a blue, hygroscopic, crystalline solid. The density varies according to the hydration, being 3.05 g mL-1 (anhydrous), 2.32 g mL-1 (trihydrate) or 2.07 g mL-1 (hexahydrate). The melting points are 256 °C for the anhydrous, 114.5 °C (trihydrate) and 26.5 °C (hexahydrate). Most of them decomposes at high temperatures. The three forms are highly soluble in water, ammonia and ethanol. They are insoluble in organic solvents as ethyl acetate.
Chemical properties: Copper (II) nitrate suffer many interesting reactions in chemical synthesis. One of this reactions is the preparation of cupric oxide by pyrolysis above 180 °C:
2 Cu(NO3)2 → 2 CuO + 4 NO2 + O2
Copper (II) nitrate can react with acetic anhydride to induce the nitration of aromatic compounds such as benzene.
Uses: Copper (II) nitrate can be used in the production of pyrotechnics and blue colors and coats. It is also used as a classical demonstration of the voltaic cell due to the redox reaction between the copper (II) nitrate and one copper electrode. Copper (II) nitrate is also uses in the production of copper (II) oxide.
Health effects / safety hazards: Copper (II) nitrate is harmful for health. It can cause irritation in throat, lungs, skin and eyes. It is noncombustible, but when mixture with wood, paper and other combustibles, it can burn.
|
Related Links: |
