Dinitrogen trioxide Formula
Dinitrogen trioxide, also known as nitrous anhydride or nitrogen sesquioxide, is a nitrogen oxide used in the preparation of other nitrogen compounds.
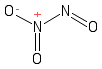
Formula and structure: The dinitrogen trioxide chemical formula is N2O3. The molar mass is 76.01 g/mol. The molecule is formed by two nitrous cation N3+ and three oxygen anions O2. The two nitrogen atoms are bound through a single bond and form the centre of the molecule. To one of the nitrogen atoms, one oxygen is bound through a single bond and the other two oxygen atoms are bound to the second nitrogen atoms through single bonds. The geometry of the molecule is planar. Its chemical structure can be written as below, in the common representations used for organic molecules.
Occurrence: Similar to other oxides of nitrogen, dinitrogen trioxide is found in the nature as being part of the biogeochemical cycle of the nitrogen in the planet. Nitrogen is found in the atmosphere, oceans and rivers and also in soils.
Preparation: Dinitrogen trioxide can be prepared from the reaction of nitrogen dioxide and nitrogen oxide. The three species are under equilibrium, so the dinitrogen trioxide cannot de isolated.
Physical properties: Dinitrogen trioxide is a blue, sharp/unpleasant odour, gas or liquid, depending on the temperature of manipulation. The density of this liquid is 1.447 g/mL, while the gas has a density of 1.738 g/mL. Its melting point is -100.7 °C and the boiling point is 3.5 °C. It is very soluble in water. Dinitrogen trioxide is also soluble in ether and other organic solvents.
Chemical properties: Dinitrogen oxide is chemically unstable. In general, this chemical compounds is found as a mixture of nitric oxide and nitrogen oxygen that are formed according to the reaction:
NO + NO2 → N2O3
This reaction takes places above the -20 °C, meaning that a room temperature, it is very difficult to get a pure and isolated dinitrogen trioxide and only at extremely low temperatures is possible to obtain it.
Uses: Dinitrogen trioxide is used in chemical laboratories in reaction of identification of terpenes. It is largely used in the preparation of other nitrogen oxygen and alkali nitrites, prepared by adding the liquid to the reaction. Dinitrogen trioxide can also be used as fuel.
Health effects / safety hazards: Dinitrogen trioxide is toxic and fatal in contact with skin or inhaled. It can also cause fires and under pressure the containers can explode if heated.
|
Related Links: |
