Acceleration Formula
Acceleration is a measure of how quickly the velocity of an object changes. So, the acceleration is the change in the velocity, divided by the time. Acceleration has a magnitude (a value) and a direction. The direction of the acceleration does not have to be the same as the direction of the velocity. The units for acceleration are meters per second squared (m/s2).

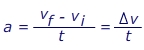
a = acceleration (m/s2)
vf = the final velocity (m/s)
vi = the initial velocity (m/s)
t = the time in which the change occurs (s)
Δv = short form for "the change in" velocity (m/s)
1) A sports car is travelling at a constant velocity v = 5.00 m/s. The driver steps on the gas, and the car accelerates forward. After 10.0 seconds, the driver stops accelerating and maintains a constant velocity v = 25.0 m/s. What was the car’s acceleration?
Answer: The initial velocity is vi = 5.00 m/s, in the forward direction. The final velocity is vf = 25.0 m/s in the forward direction. The time in which this change occurred is 10.0 s. The acceleration is in the forward direction, with a value:
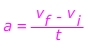
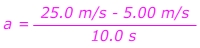
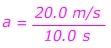
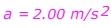
The car's acceleration is 2.00 m/s2, forward.
2) A child drops a rock off of a cliff. The rock falls for 15.0 s before hitting the ground. The acceleration due to gravity is g = 9.80 m/s2. What was the velocity of the rock the instant before it hit the ground?
Answer: The rock was released from rest, so the initial velocity is vi = 0.00 m/s. The time in which the change occurred is 15.0 s. The acceleration is 9.80 m/s2. The final velocity must be found, so rearrange the equation:
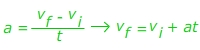
vf = vi + at
vf = 0.00 m/s +(9.80 m/s2)(15.0 s)
vf = 147 m/s
The rock is falling, so the direction of the velocity is down.
|
Related Links: Acceleration Quiz Acceleration Practice Problems Quiz Force and Acceleration Quiz Acceleration Conversion |
